When Should The Rescuer Operating The AED Clear The Victim
When should the rescuer operating the aed clear the victim?
A fantastic feature in the face of the worst disaster or negative event is the ability to act fast yet efficiently.
Nowhere are these voices more important than in such instances where one of the essential life-saving devices, the Automated External Defibrillator (AED), is used.
Now, this life-saving tool, which not only identifies sudden cardiac arrest but also treats the affected patient, has become an integral part of any emergency response.
However, using an AED properly entails some steps and protection measures to minimize the danger that a rescuer or the patient might encounter in the course of facilitating the intervention.
As a frequent reader of this website, you will be able to take a tour of how a rescuer should clear a victim while using an AED as well as other important techniques in performing CPR.
Understanding The AED and Its Operation
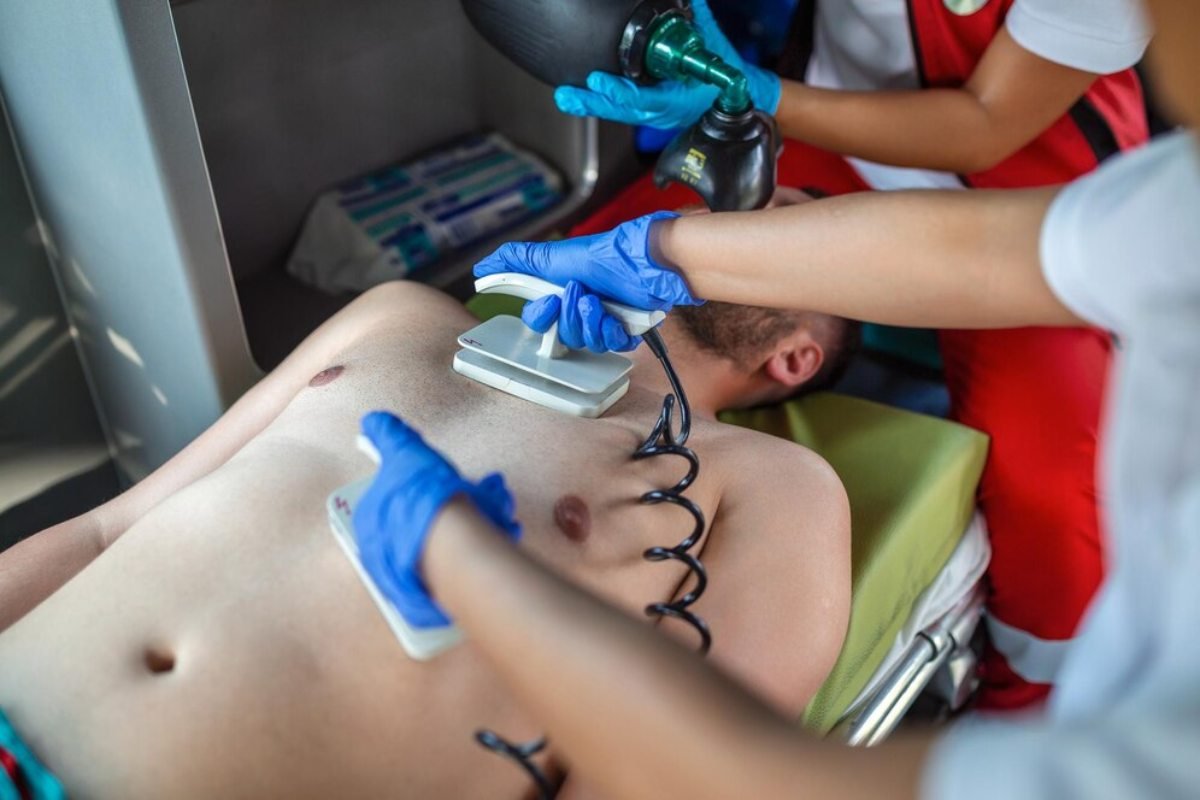
An AED is known as an Automatic External Defibrillator which is a portable instrument used to monitor critical heart diseases which are called Cardiac Arrest to diagnose as well as treat using an electric shock called defibrillation to correct the heart rhythm.
In order for the AED to function as designed and to rescue the victim safely the rescuer has to adhere to a prescribed sequence of actions contained in the control algorithm which addresses the critical step of the rescuer clearing the victim.
When Should The Rescuer Operating The AEd Clear The Victim?
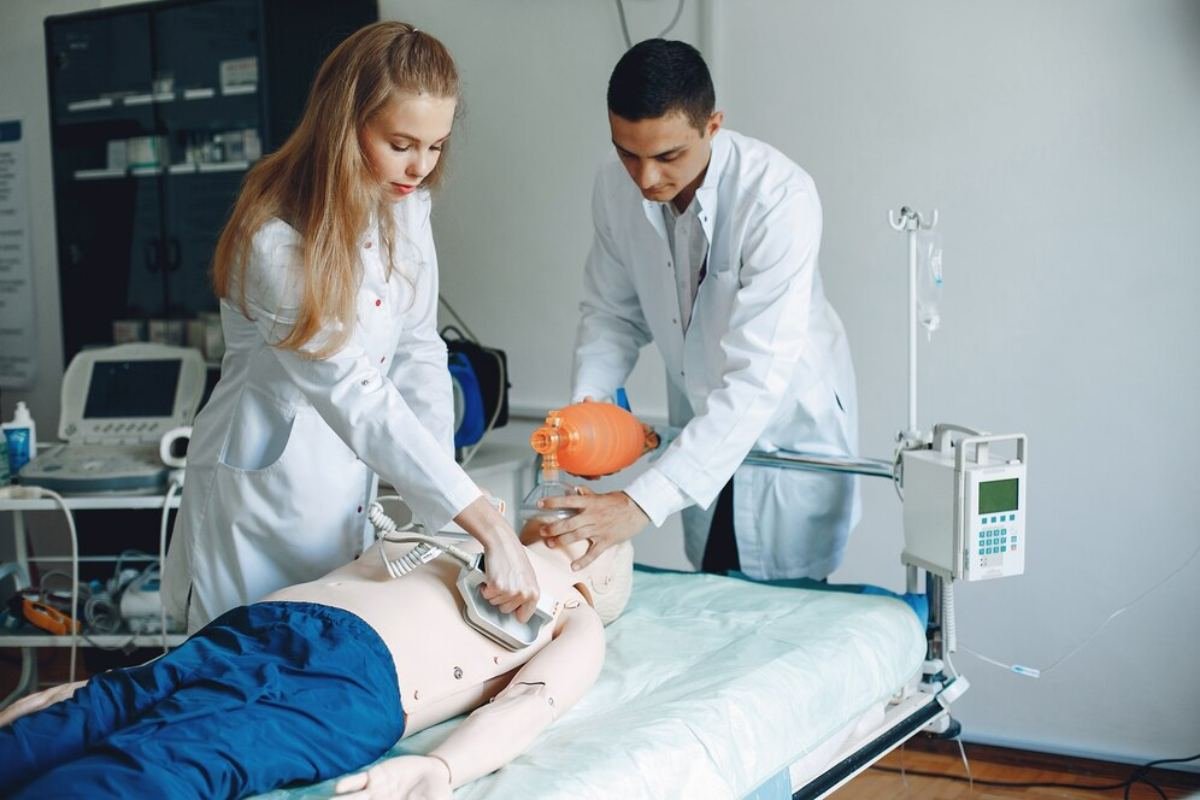
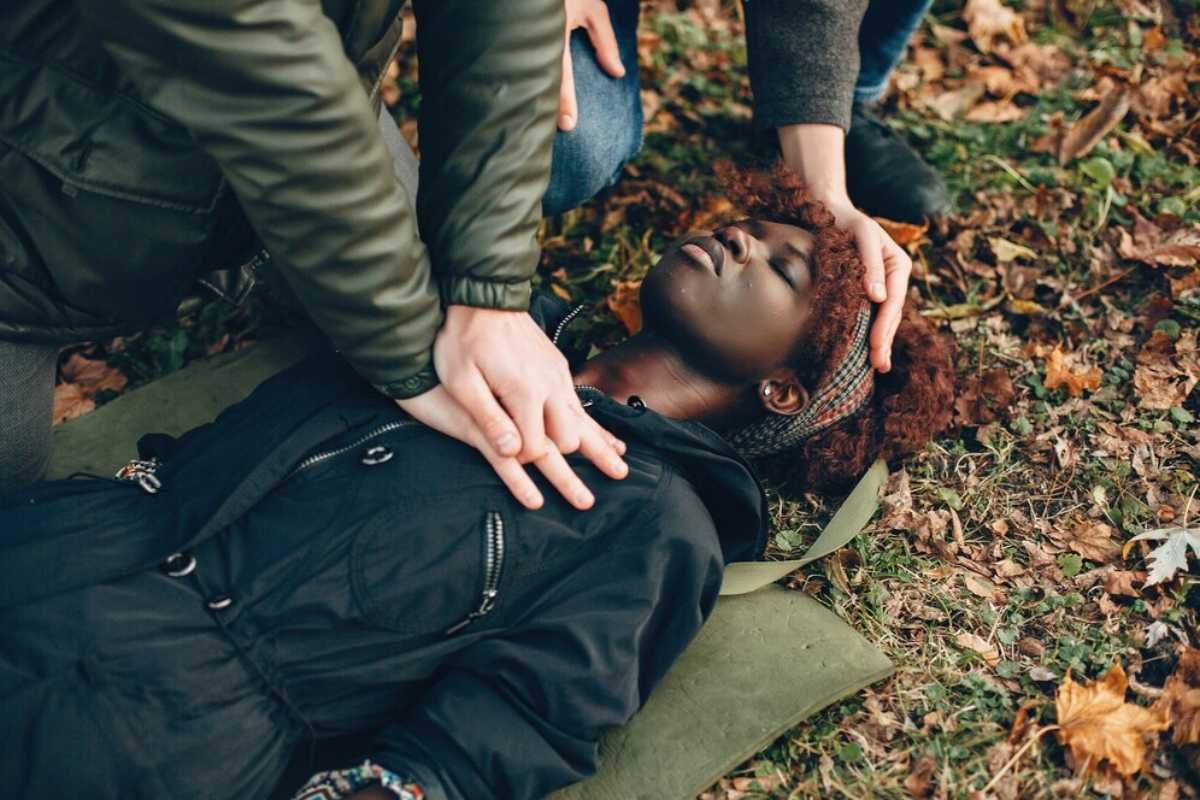
The mere fact that it is necessary to clear the victim points to the fact this maneuver has to be performed most adequately in order to avoid any harm to the people involved.
Here are the key moments when the rescuer must clear the victim.
During Analysis
You, if the AED pads have been connected to the chest of the victim and the device, is now monitoring the heartbeat.
While undertaking the Resuscitation-CPR quality improvement checklist analysis phase, the rescuer should also make sure that none of his or her members or he/she is touching the victim.
Touch or motion may pose a problem since it is likely to affect the ability of AEDs to identify the abnormal heart rhythm.
Before Delivering a Shock
The chest compressions performed by the rescuer are interrupted if the AED decides that a shock is needed.
They must shout, “Clear!” thrice and ensure that there is no contact between the victim and the water before pressing the shock button.
This step is aimed at avoiding any danger of electrical shock to either the rescuer or any other onlooker present.
After Delivering a Shock
Aftershock, the AED may recommend the rescuer to perform CPR.
Before proceeding to chest compressions or rescue breaths, it is advisable that the rescuer checks once more that the victim is not inhibited in any way.
This technique involves using a bag-mask to deliver breaths The water content in the lungs could be retained by using a bag-mask technique Special attention is required minute-by-minute when a patient is unconscious to ensure that the delivery of breaths is done effectively.
When providing rescue breaths with a bag-mask device, the rescuer must follow specific steps to ensure effective ventilation.
Positioning: The rescuer should stand where its head touches the victim including covering the victim’s mouth and nose with the mask.
Technique: The rescuer uses the “E-C” clamp technique to hold the mask in place: It is folded on the sides by forming the letter “E” on the side part of the mask by joining the four fingers while the thumb and the index finger forms a “C” at the top part of the mask.
This grip ensures that the mouthpiece does not come in contact with any other metal thereby ensuring that no air gets in between.
Breaths: Ideally, the rescuer should take approximately one second to blow into the face mask to ensure the stale air is exhaled out while observing the rise of the victim’s chest to confirm proper ventilation has occurred.
Post-AED Shock Procedures
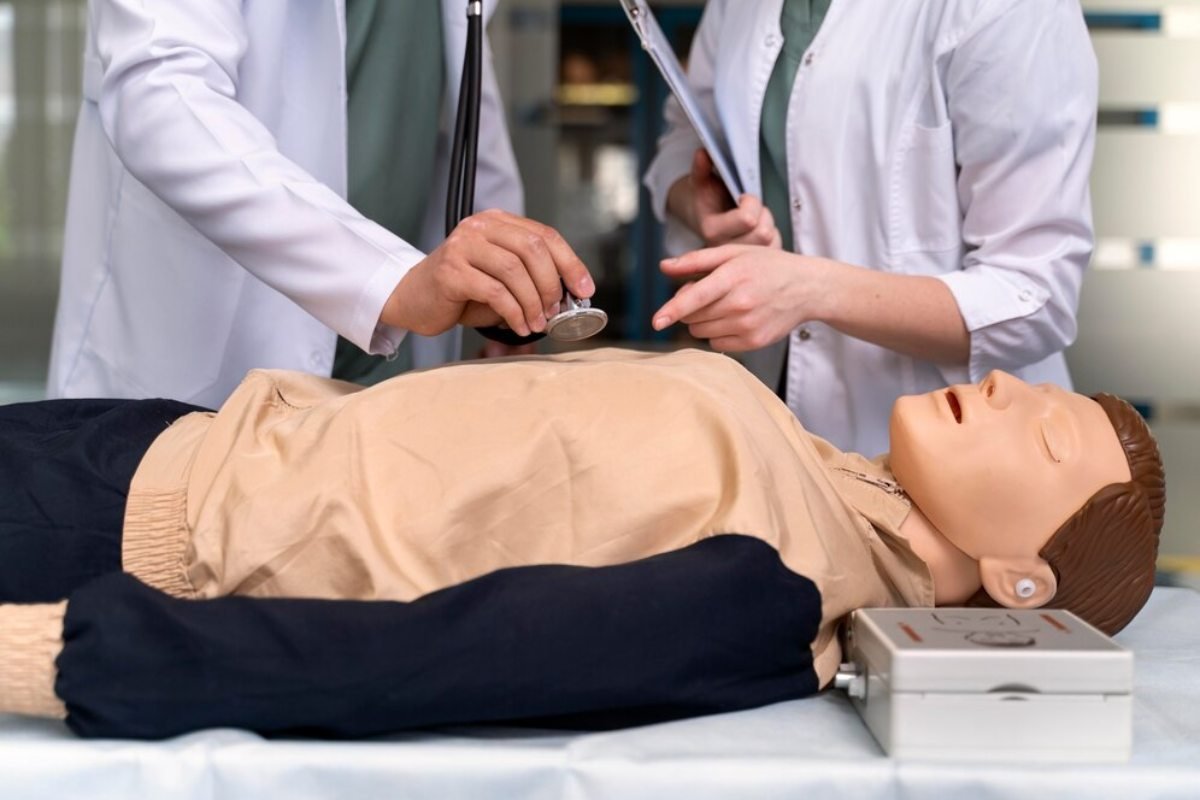
Prompted by this, the resuscitator should commence chest compressions soon after the provision of a shock by the AED.
The health-related high-quality CPR for emitting compressions is recommended to be at the rate of 100-120 per minute and that of depth to be at least 2 inches for the adults, with full recoil of the chest in between.
Attaching AED Pads Before Starting CPR
While commencing CPR, AED pads should be first connected. The subject matter of this rationale is well justified based on the following reasons.
In emergency situations, such as sudden cardiac arrest, time is one of the essential factors on which the chances of survival significantly depend.
The rescuer should place the AED pick-up pads on the victim’s bare chest as early as possible.
This action ensures that the AED is in a position to interpret the heartbeat and determine if a shock is required.
A rescuer should presume to perform CPR only after the AED pads have been connected in case he or she gets advised to do so.
Using a Pocket Mask
In the case of administration of rescue breaths utilizing a pocket mask, the rescuer must be situated at the head of the victim.
This position enables the rescuer to use both hands to adequately hold the mask in place ensuring that there is a blower chamber and at the same time have a vantage view of the chest area so as to check for rise when delivering an airway breath.
May You Like Also: How Long Does It Take For Antibiotics To Start Working?
Conclusion
Learning proper usage of an AED as well as CPR will enhance the rates of survival for any patient who has experienced a cardiac arrest.
What is related to range of motion or movements: During heart rhythm exclude the victim during any check, before and after shock delivery, after each cycle.
The cohort demonstrated control of providing breaths with a bag-mask, attaching the AED pads, and handling a pocket mask.
These skills ensure that when conductors go inside the trains, they do so cool-headed and lots of people might be saved.
You May Like Also:












